Last night, the CDC updated some of their COVID19 recommendations.
Double masks work better.
This isn’t surprising and we were expecting this recommendation to come down the pipeline. From previous research we know that masks work to some degree. Over 80 studies have been done on this. However, we haven’t been too sure about the effectiveness of different TYPES of masks. One previous study said that single layer cloth masks work <20% of the time; two-layered masks work about 40% of the time; and N95’s work 95% of the time (hence the 95 in N95). Yesterday, the CDC published a study that found a few key things…
In terms of blocking COVID19 virus particles…
Medical procedure mask alone blocked 42% of particles
A cloth mask alone blocked 44.3% of particles
Double masks (a surgical mask combined with a cloth mask) blocks 92.5% of COVID19 particles.
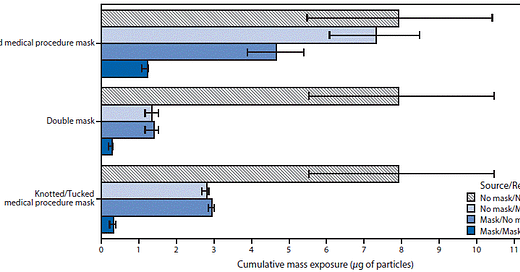
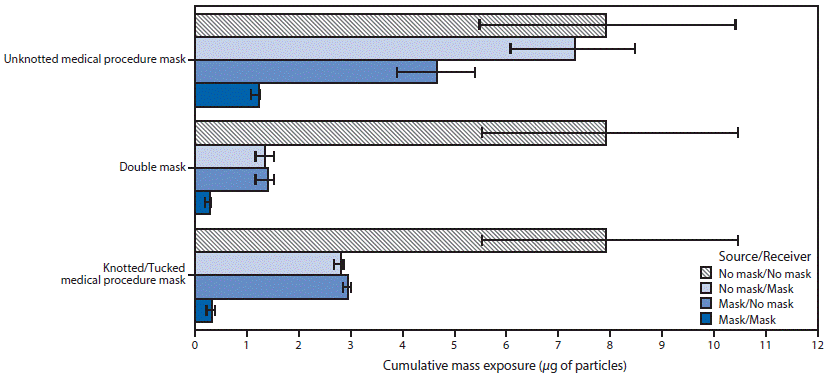
In terms of exposure to COVID19…
A medical procedure mask along with knotted ear loops AND tucked in sides, reduced exposure of COVID19 by 62.9%
When the source and receiver were both fitted with double masks, exposure of the receiver was reduced 96.4%. That’s huge.
Bottom line: Masks work. Double masks work much better.
People with a known (diagnosed) PEG , polysorbate, or other vaccine ingredient allergy should NOT get the Moderna or Pfizer vaccine.
We are also not surprised about this recommendation either. A previous post of mine explained PEG in vaccines…
PEG has never been used before in an approved vaccine, but it is found in many drugs (and toothpaste and shampoo) that have occasionally triggered anaphylaxis. This is particularly true among people who already have high levels of anti-PEG antibodies or experienced severe allergic reactions in the past. Although many types of nanoparticles do have hypersensitivity properties, some newer nanoparticles have been demonstrating ANTI-allergic effects. Controlling the pro and anti-allergic properties of nanoparticles is one of the key elements towards safe use. The U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases had a meeting mid-December to discuss the COVID19 vaccine allergic reactions and is conducting several studies on it to better understand why people with previous history may have allergic reactions with Pfizer/Moderna COVID19 vaccines. Since this meeting there have been 50 anaphylaxis cases reported for Pfizer (out of 9.943M doses) and 21 reported for Moderna (out of 7.581M doses). This is an anaphylaxis rate of 5 in 1M people (or 0.000503%). This IS higher than the rate of anaphylactic reactions that happen with any other vaccine (1 in 1M people).
FYI… Polysorbate is NOT an ingredient in the vaccines, but closely related to PEG. So this is a precaution. Here are the other ingredients in the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines (see Appendix C).
Public health recommendations for vaccinated people
This is where the new recommendations get confusing. I think this section could have been worded much clearer.
It’s important to note that the first sentence of this recommendation is: “There is currently limited information on how much the vaccines might reduce transmission and how long protection lasts”. THEN the CDC goes on to recommend that people with the vaccine do NOT need to quarantine after known COVID19 exposure if you…
Are fully vaccinated (i.e., ≥2 weeks following receipt of the second dose in a 2-dose series)
Are within 3 months following receipt of the last dose in the series
Have remained asymptomatic since the current COVID-19 exposure
This, naturally, has people asking the following two questions…
Do antibodies only last 3 months? NO. We know they last longer after a “natural” infection. Several studies have shown antibodies last up to 8 months (this is because the studies were only 8 months long). We are at the mercy of time. There is no reason to think that natural antibodies last LONGER than vaccine antibodies. But the CDC said 3 months because we only have 3 months of antibody follow-up data for vaccines.
Do vaccines reduce transmission? We still do not know about this. We have three small beacons of light that transmission is reduced by about 60%, but we don’t have enough evidence to be definitive. We saw these hints in the Moderna trial and, most recently, in the AstraZeneca trial. We are still waiting for our “ah ha” study to show reduced transmission.
Love, YLE


I’m still so confused why fully vaccinated people don’t need to quarantine if we don’t have good data about transmission from vaccinated ppl?
Thank you so much. You are keeping me updated with great information. It's was sooooo upsetting last week when you got hacked. I am glad you are back. Keep up the great work 😊