Okay, this update is heavy but important. As always, peach boxes=additions since my last table update. Explanations and data sources are below.
Moderna
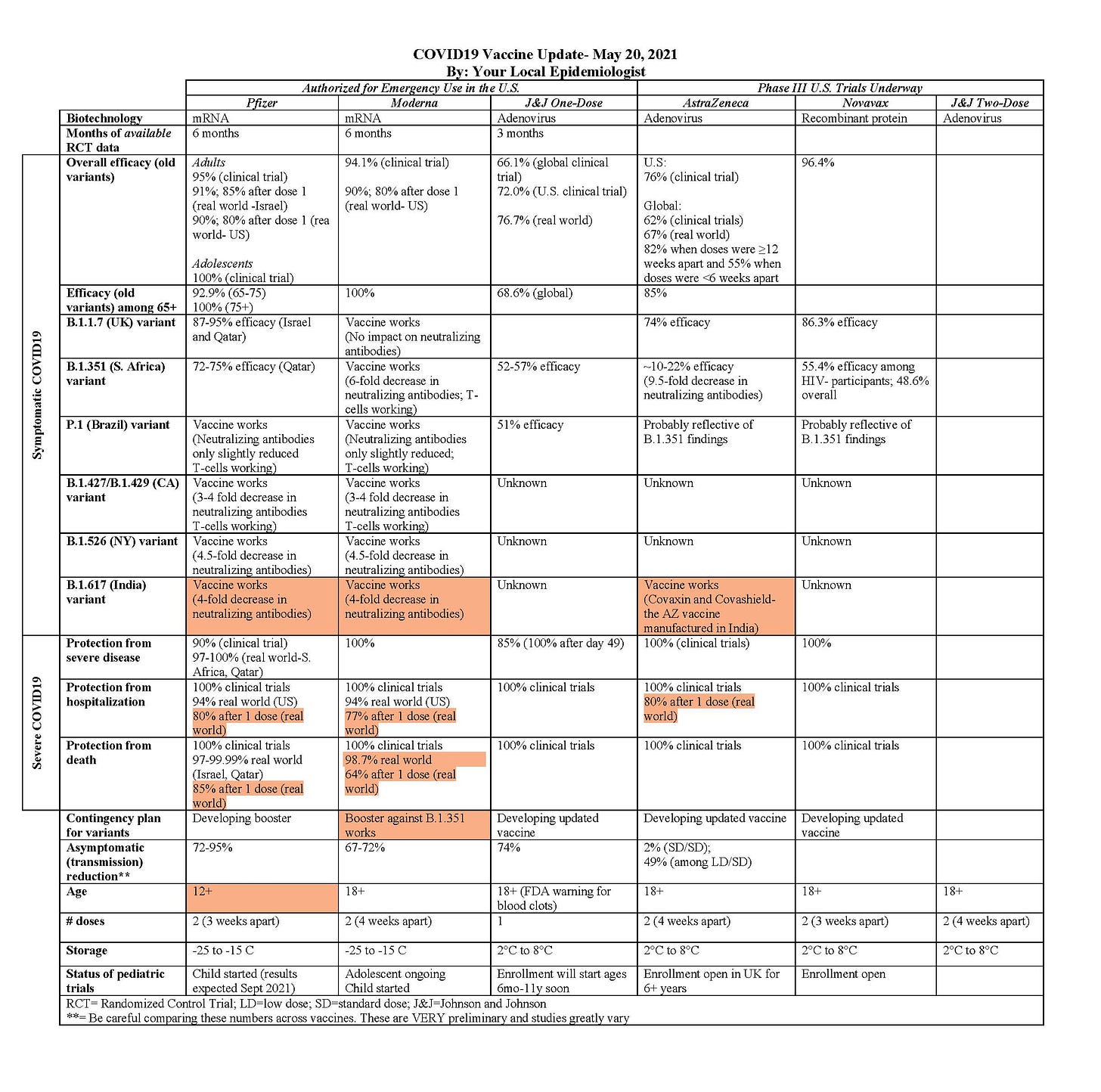
Works against B.1.617 variant (here)
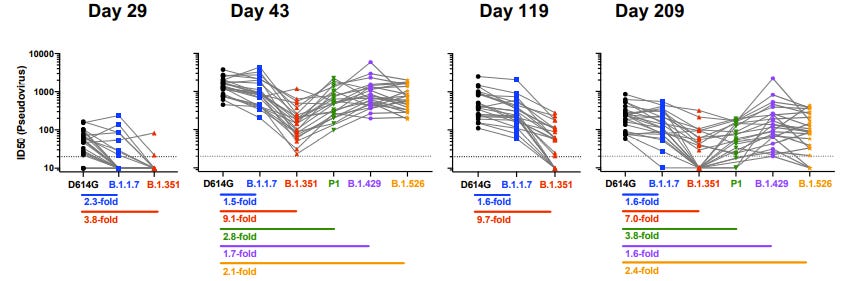
Working against all variants of concern (here) for at least 6 months. It’s important to note that this study was only 6 months long, meaning Moderna likely lasts longer. This is great news.
In the “real world”, Moderna was 98.7% effective against death after both doses; 64% effective against death after 1 dose. Moderna was 77% effective in preventing hospitalization after 1 dose (here)
Moderna booster shot works (previous post on this here)
Pfizer
Works against B.1.617 variant (here)
One dose was 80% effective at preventing hospital admission with COVID-19
and one dose was 85% effective at preventing death (here)
AstraZeneca
Covashield (the AstraZeneca vaccine manufactured in India) and Covaxin works well against B.1.617 variant (here)
One dose was 80% effective at preventing hospital admission with COVID-19 (here)
We are still waiting to see the “real world” efficacy of AZ against severe disease of B.1.351 (variant first discovered in S. Africa). The only number we have is ~10-22% for mild-to-moderate disease, but there weren’t enough COVID19 cases to be certain in this efficacy rate.
All vaccines
There are two ways to measure how well a vaccine works: Efficacy and immunogenicity. Immunogenicity is a more complicated metric that measures the type of immune responses that the vaccine generates and their magnitude over time (i.e. neutralizing antibodies). Until now, there was no definitive set values that “define” a protective immune response. We weren’t sure how neutralizing antibodies in a lab mapped to efficacy rate in the real world. A new, very important article (here) modeled for the first time the relationship. We can now use this mathematical model and my table together. For example…
Moderna had a 94% efficacy rate during the clinical trials (before variants). After a lab study, Moderna had a 3-4 fold decrease in neutralizing antibodies against B.1.526. According to the mathematical model, that would mean a Moderna efficacy rate of ~70% in the real world.
AstraZeneca efficacy in the United States during clinical trials (before variants) was 76%. After a lab study, AZ had a 9.5-fold decrease in neutralizing antibodies against B.1.351. According to the model, that would mean a AZ efficacy rate of ~20% in the real world.
Love, YLE



ah, thank you for the lots-of-good-news update! And for the table that finally gave me a picture of what '5-fold decrease' actually means mathematically - whew, not as scary as the number sounded to me! One picky detail on your vaccine table - Pfizer should now be 12+ rather than 16+, yes?
Table still says ages 16+ for Pfizer.